Buying a House: the Budget 2
Buying a House: the Budget 2
For example, “Flat 35” (a mortgage loan provided by the Japan Housing Finance Agency (JHF) in partnership with private financial institutions) stipulates that the loan amount must be between 1 million yen and 80 million yen (in units of 10,000 yen), within the construction or purchase price. The ratio of the annual repayment amount to annual income including tax is also defined as shown in the table below.
However, this is only the standard for “Flat 35”. The amount of money that can be repaid depends on each household’s financial situation. For example, you may need money for your child’s education or for your parent’s nursing care, or you may want to buy a new car. you should determine the amount you can borrow after considering your individual circumstances and knowing the maximum amount of repayment for your family budget.
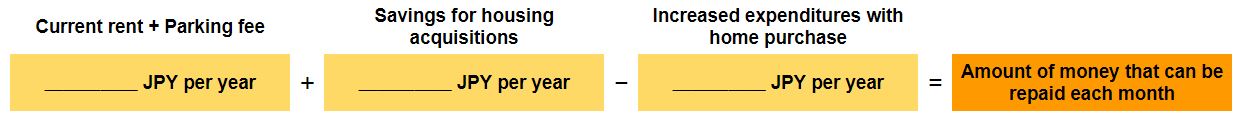
First, review your current household income and expenditures, and identify the amount of monthly household surplus that can be used to repay the loan, including the amount of expenditures and reserves that will decrease as a result of the home purchase. Next, subtract the expected increase in expenses due to the purchase of the house from this amount, and estimate the amount that can be repaid each month. However, it is safer to consider this amount as the maximum amount and to plan your repayment with a little extra time to spare.
- How to calculate the amount of expenditure that will decrease after purchasing a house
(Example): Current housing expenses (rent and management fees + parking lot fees) + the amount of savings you are making for home acquisition
- How to calculate the amount of expenses that will increase after purchasing a house
(Example): Taxes + maintenance and repair reserve fund + parking lot fee + utility expenses (amount expected to increase due to a change of residence)
* *As for the amount of taxes, management fees and reserve for repairs (in the case of condominiums), ask the real estate agency for a rough estimate once you have decided on a potential purchase property.
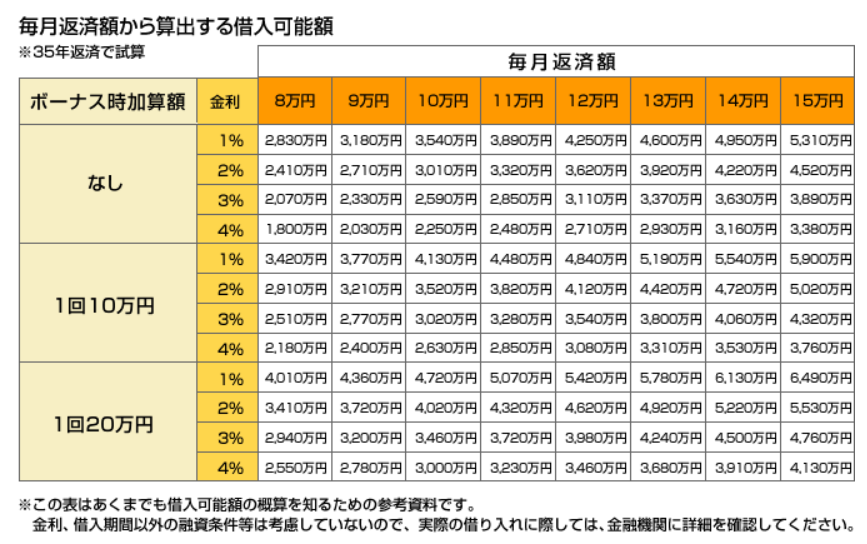
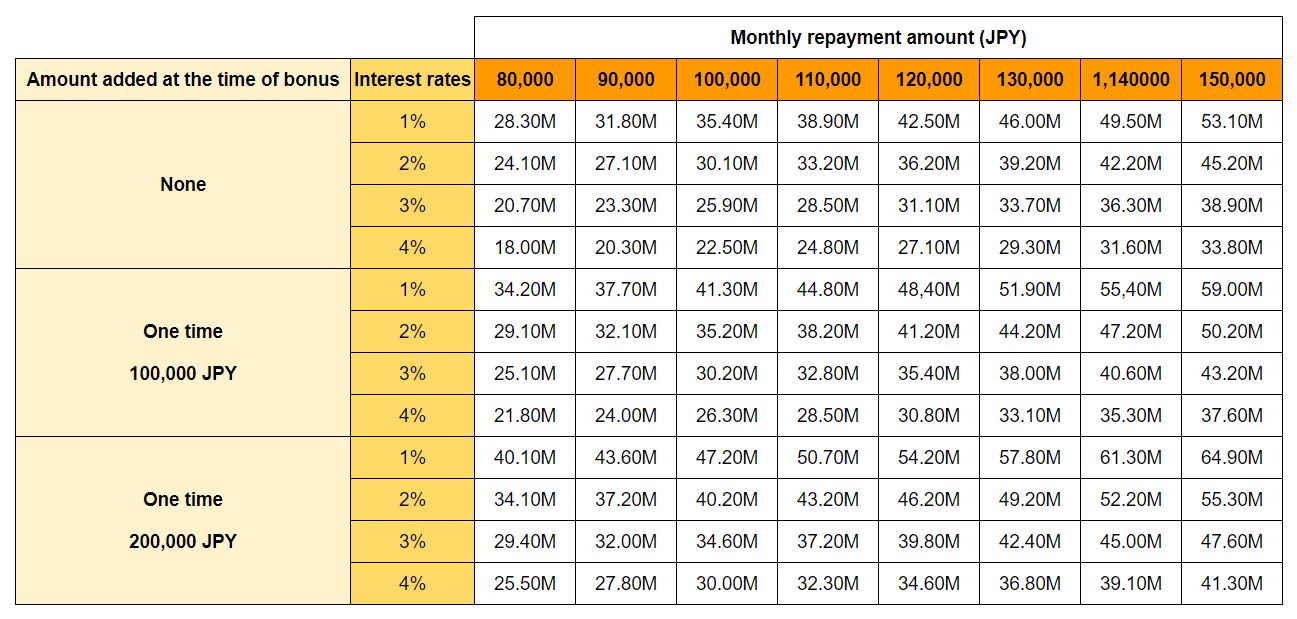
For example, if the monthly repayment is 80,000 yen, the bonus repayment is zero yen, the interest rate is 2%, and the repayment is over 35 years, the amount that can be borrowed is 24,100,000 yen. Although you should not rely too heavily on bonuses, you may want to consider using bonus repayments if the amount paid is expected to be somewhat stable.
A simulation that calculates the amount that can be borrowed based on annual income and monthly repayments is available on the Internet and can be entered to find out.
The important thing is to consider your financial plan with this borrowing capacity as the “upper limit. Be sure to plan your finances carefully, assuming a decrease in income, an increase in expenses, and, in the case of a loan with variable interest rates, an increase in repayments due to a rise in interest rates.
*Calculated based on 35-year repayment
Please confirm the details with the financial institution when actually borrowing funds.